全部的 K8S学习笔记总目录 ,请点击查看。
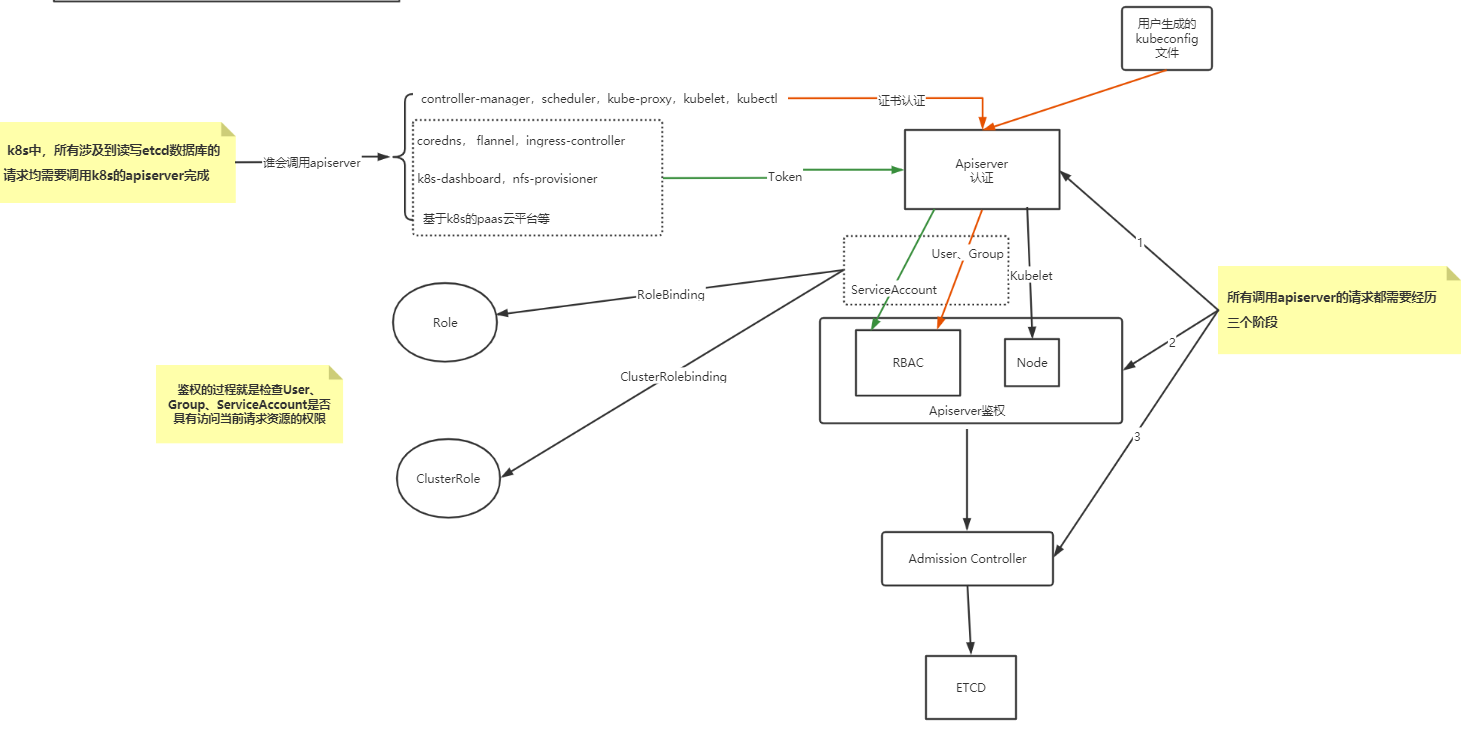
Kubernetes 有一个内建的 Role-based access control (RBAC) 机制,它可以控制用户对 Kubernetes API 的访问权限。RBAC 机制可以让集群管理员控制用户、服务账户和组对 Kubernetes API 的访问权限。
APIServer安全控制
Authentication:身份认证
这个环节它面对的输入是整个http request,负责对来自client的请求进行身份校验,支持的方法包括:
basic authclient证书验证(https双向验证)
jwt token(用于serviceaccount)
APIServer启动时,可以指定一种Authentication方法,也可以指定多种方法。如果指定了多种方法,那么APIServer将会逐个使用这些方法对客户端请求进行验证, 只要请求数据通过其中一种方法的验证,APIServer就会认为Authentication成功;
使用kubeadm引导启动的k8s集群,apiserver的初始配置中,默认支持client证书验证和serviceaccount两种身份验证方式。 证书认证通过设置--client-ca-file根证书以及--tls-cert-file和--tls-private-key-file来开启。
在这个环节,apiserver会通过client证书或 http header中的字段(比如serviceaccount的jwt token)来识别出请求的用户身份,包括”user”、”group”等,这些信息将在后面的authorization环节用到。
Authorization:鉴权,你可以访问哪些资源
这个环节面对的输入是http request context中的各种属性,包括:user、group、request path(比如:/api/v1、/healthz、/version等)、 request verb(比如:get、list、create等)。
APIServer会将这些属性值与事先配置好的访问策略(access policy)相比较。APIServer支持多种authorization mode,包括Node、RBAC、Webhook等。
APIServer启动时,可以指定一种authorization mode,也可以指定多种authorization mode,如果是后者,只要Request通过了其中一种mode的授权, 那么该环节的最终结果就是授权成功。在较新版本kubeadm引导启动的k8s集群的apiserver初始配置中,authorization-mode的默认配置是”Node,RBAC”。
Admission Control:准入控制 ,一个控制链(层层关卡),用于拦截请求的一种方式。偏集群安全控制、管理方面。 为什么需要? 认证与授权获取 http 请求 header 以及证书,无法通过body内容做校验。
Admission 运行在 API Server 的增删改查 handler 中,可以自然地操作 API resource
举个栗子 LimitRanger 修改LimitRanger大小,若集群的命名空间设置了LimitRange对象,且Pod声明时未设置资源值,则按照LimitRange的定义来为Pod添加默认值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 apiVersion: v1 kind: LimitRange metadata: name: mem-limit-range namespace: demo spec: limits: - default: memory: 512Mi defaultRequest: memory: 256Mi type: Container --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: default-mem-demo namespace: demo spec: containers: - name: default-mem-demo image: nginx:alpine
查看认证情况
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 $ kubectl -v=7 create namespace demo I1023 11:45:34.937311 1367593 loader.go:395] Config loaded from file: /home/aaron/.kube/config I1023 11:45:34.940024 1367593 round_trippers.go:463] POST https://192.168.100.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces?fieldManager=kubectl-create&fieldValidation=Strict I1023 11:45:34.940086 1367593 round_trippers.go:469] Request Headers: I1023 11:45:34.940121 1367593 round_trippers.go:473] Accept: application/json, */* I1023 11:45:34.940154 1367593 round_trippers.go:473] Content-Type: application/json I1023 11:45:34.940200 1367593 round_trippers.go:473] User-Agent: kubectl/v1.28.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/855e7c4 I1023 11:45:34.971203 1367593 round_trippers.go:574] Response Status: 201 Created in 30 milliseconds namespace/demo created $ kubectl -v=7 apply -f mem-limit-range.yaml I1023 11:46:54.566053 1368262 loader.go:395] Config loaded from file: /home/aaron/.kube/config I1023 11:46:54.568879 1368262 round_trippers.go:463] GET https://192.168.100.1:6443/openapi/v2?timeout =32s I1023 11:46:54.568933 1368262 round_trippers.go:469] Request Headers: I1023 11:46:54.568987 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Accept: application/com.github.proto-openapi.spec.v2@v1.0+protobuf I1023 11:46:54.569036 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] User-Agent: kubectl/v1.28.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/855e7c4 I1023 11:46:54.608556 1368262 round_trippers.go:574] Response Status: 200 OK in 39 milliseconds I1023 11:46:54.835559 1368262 round_trippers.go:463] GET https://192.168.100.1:6443/openapi/v3?timeout =32s I1023 11:46:54.835626 1368262 round_trippers.go:469] Request Headers: I1023 11:46:54.835663 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] User-Agent: kubectl/v1.28.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/855e7c4 I1023 11:46:54.835713 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Accept: application/json, */* I1023 11:46:54.839142 1368262 round_trippers.go:574] Response Status: 200 OK in 3 milliseconds I1023 11:46:54.842249 1368262 round_trippers.go:463] GET https://192.168.100.1:6443/openapi/v3/api/v1?hash =64470CFAF8CA1AC72CDF17D98F7AB1B4FA6357371209C6FBEAA1B607D1B09E70C979B0BA231366442A884E6888CF86F0205FF562FCA388657C7250E472112154&timeout =32s I1023 11:46:54.842307 1368262 round_trippers.go:469] Request Headers: I1023 11:46:54.842340 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Accept: application/json I1023 11:46:54.842372 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] User-Agent: kubectl/v1.28.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/855e7c4 I1023 11:46:54.845368 1368262 round_trippers.go:574] Response Status: 200 OK in 2 milliseconds I1023 11:46:55.190015 1368262 round_trippers.go:463] GET https://192.168.100.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/demo/limitranges/mem-limit-range I1023 11:46:55.190086 1368262 round_trippers.go:469] Request Headers: I1023 11:46:55.190179 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Accept: application/json I1023 11:46:55.190253 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] User-Agent: kubectl/v1.28.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/855e7c4 I1023 11:46:55.195521 1368262 round_trippers.go:574] Response Status: 404 Not Found in 5 milliseconds I1023 11:46:55.196192 1368262 round_trippers.go:463] GET https://192.168.100.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/demo I1023 11:46:55.196256 1368262 round_trippers.go:469] Request Headers: I1023 11:46:55.196290 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Accept: application/json I1023 11:46:55.196319 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] User-Agent: kubectl/v1.28.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/855e7c4 I1023 11:46:55.200893 1368262 round_trippers.go:574] Response Status: 200 OK in 4 milliseconds I1023 11:46:55.201301 1368262 round_trippers.go:463] POST https://192.168.100.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/demo/limitranges?fieldManager=kubectl-client-side-apply&fieldValidation=Strict I1023 11:46:55.201365 1368262 round_trippers.go:469] Request Headers: I1023 11:46:55.201398 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Accept: application/json I1023 11:46:55.201444 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Content-Type: application/json I1023 11:46:55.201485 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] User-Agent: kubectl/v1.28.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/855e7c4 I1023 11:46:55.212289 1368262 round_trippers.go:574] Response Status: 201 Created in 10 milliseconds limitrange/mem-limit-range created I1023 11:46:55.212851 1368262 round_trippers.go:463] GET https://192.168.100.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/demo/pods/default-mem-demo I1023 11:46:55.212931 1368262 round_trippers.go:469] Request Headers: I1023 11:46:55.213019 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Accept: application/json I1023 11:46:55.213077 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] User-Agent: kubectl/v1.28.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/855e7c4 I1023 11:46:55.217515 1368262 round_trippers.go:574] Response Status: 404 Not Found in 4 milliseconds I1023 11:46:55.217783 1368262 round_trippers.go:463] GET https://192.168.100.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/demo I1023 11:46:55.217866 1368262 round_trippers.go:469] Request Headers: I1023 11:46:55.217903 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Accept: application/json I1023 11:46:55.217958 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] User-Agent: kubectl/v1.28.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/855e7c4 I1023 11:46:55.222263 1368262 round_trippers.go:574] Response Status: 200 OK in 4 milliseconds I1023 11:46:55.222547 1368262 round_trippers.go:463] POST https://192.168.100.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/demo/pods?fieldManager=kubectl-client-side-apply&fieldValidation=Strict I1023 11:46:55.222608 1368262 round_trippers.go:469] Request Headers: I1023 11:46:55.222657 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Content-Type: application/json I1023 11:46:55.222694 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] User-Agent: kubectl/v1.28.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/855e7c4 I1023 11:46:55.222727 1368262 round_trippers.go:473] Accept: application/json I1023 11:46:55.230761 1368262 round_trippers.go:574] Response Status: 201 Created in 7 milliseconds pod/default-mem-demo created I1023 11:46:55.231543 1368262 apply.go:535] Running apply post-processor function
NodeRestriction 此插件限制kubelet修改Node和Pod对象,这样的kubelets只允许修改绑定到Node的Pod API对象,以后版本可能会增加额外的限制 。开启Node授权策略后,默认会打开该项
怎么使用?
APIServer启动时通过 --enable-admission-plugins --disable-admission-plugins 指定需要打开或者关闭的 Admission Controller
主要使用场景是以下几种:
自动注入sidecar容器或者initContainer容器
webhook admission,实现业务自定义的控制需求
kubectl的认证授权 kubectl的日志调试级别:
信息
描述
v=0
通常,这对操作者来说总是可见的。
v=1
当您不想要很详细的输出时,这个是一个合理的默认日志级别。
v=2
有关服务和重要日志消息的有用稳定状态信息,这些信息可能与系统中的重大更改相关。这是大多数系统推荐的默认日志级别。
v=3
关于更改的扩展信息。
v=4
调试级别信息。
v=6
显示请求资源。
v=7
显示 HTTP 请求头。
v=8
显示 HTTP 请求内容。
v=9
显示 HTTP 请求内容,并且不截断内容。
1 2 3 $ kubectl get nodes -v=7 I0329 20:20:08.633065 3979 loader.go:359] Config loaded from file /root/.kube/config I0329 20:20:08.633797 3979 round_trippers.go:416] GET https://10.209.0.13:6443/api/v1/nodes?limit =500
kubeadm init启动完master节点后,会默认输出类似下面的提示内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ... ... Your Kubernetes master has initialized successfully! To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME /.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME /.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME /.kube/config ... ...
这些信息是在告知我们如何配置kubeconfig文件。按照上述命令配置后,master节点上的kubectl就可以直接使用$HOME/.kube/config的信息访问k8s cluster了。 并且,通过这种配置方式,kubectl也拥有了整个集群的管理员(root)权限。
很多K8s初学者在这里都会有疑问:
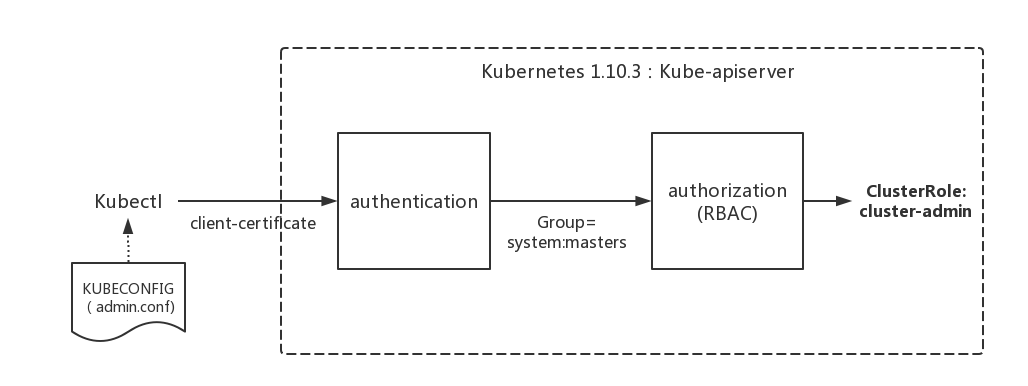
当kubectl使用这种kubeconfig方式访问集群时,Kubernetes的kube-apiserver是如何对来自kubectl的访问进行身份验证(authentication)和授权(authorization)的呢?
为什么来自kubectl的请求拥有最高的管理员权限呢?
查看$HOME/.kube/config文件:
前面提到过apiserver的authentication支持通过tls client certificate、basic auth、token等方式对客户端发起的请求进行身份校验, 从kubeconfig信息来看,kubectl显然在请求中使用了tls client certificate的方式,即客户端的证书。
证书base64解码:
1 $ echo xxxxxxxxxxxxxx |base64 -d > kubectl.crt
说明在认证阶段,apiserver会首先使用--client-ca-file配置的CA证书去验证kubectl提供的证书的有效性,基本的方式 :
1 2 $ openssl verify -CAfile /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt kubectl.crt kubectl.crt: OK
除了认证身份,还会取出必要的信息供授权阶段使用,文本形式查看证书内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 $ openssl x509 -in kubectl.crt -text Certificate: Data: Version: 3 (0x2) Serial Number: 753391350411361453 (0xa7495710a1efcad) Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption Issuer: CN = kubernetes Validity Not Before: Aug 25 07:12:13 2023 GMT Not After : Aug 24 07:17:20 2024 GMT Subject: O = system:masters, CN = kubernetes-admin ...
认证通过后,提取出签发证书时指定的CN(Common Name),kubernetes-admin,作为请求的用户名 (User Name), 从证书中提取O(Organization)字段作为请求用户所属的组 (Group),group = system:masters,然后传递给后面的授权模块。
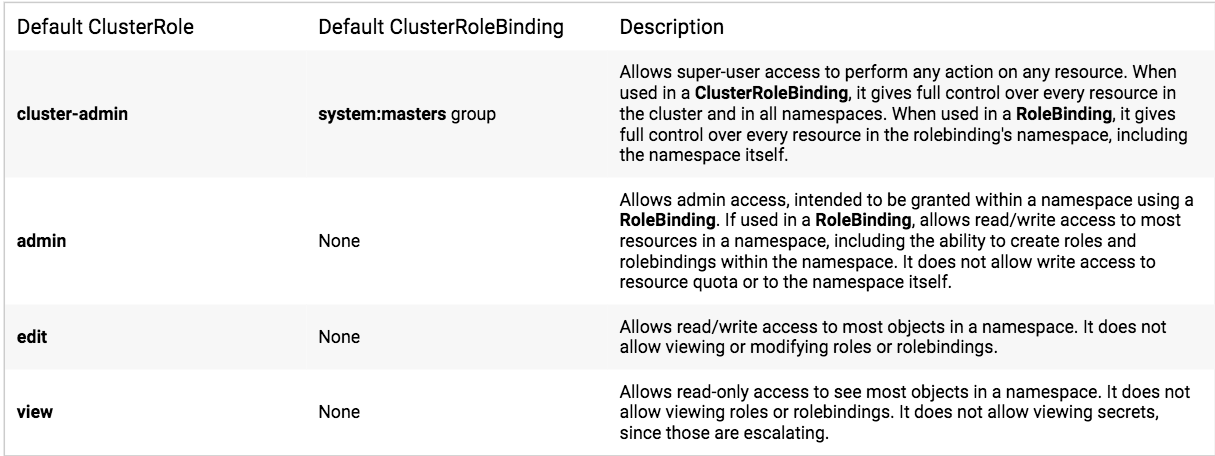
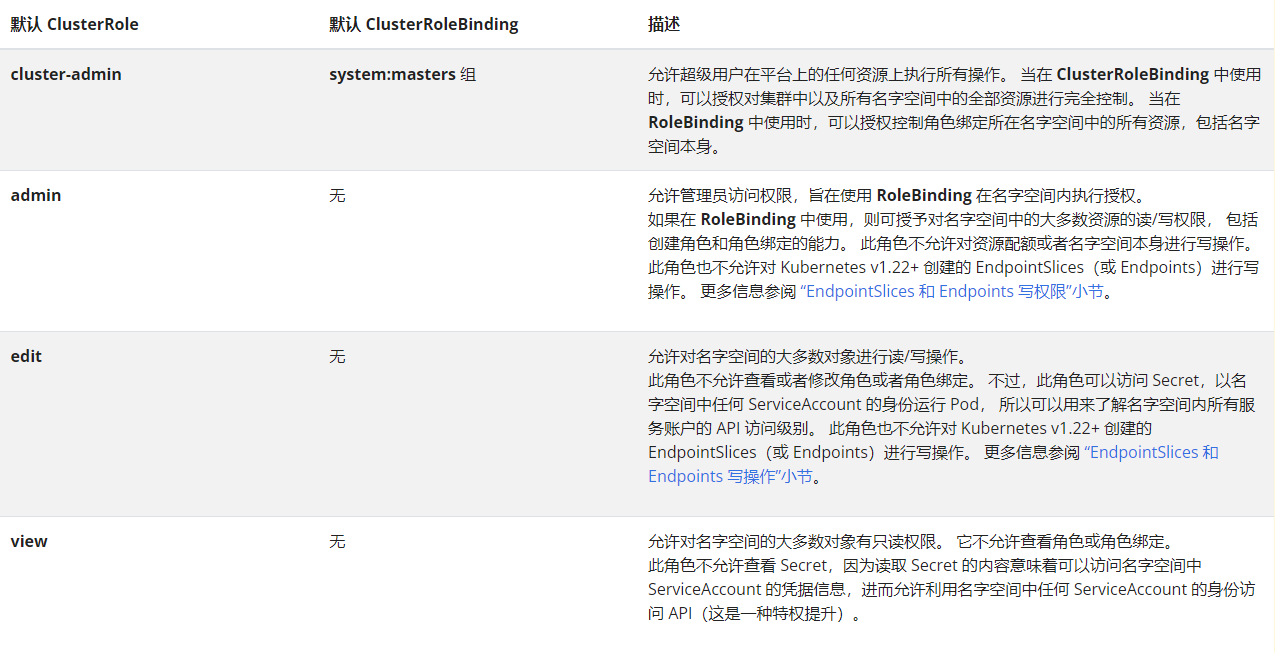
kubeadm在init初始引导集群启动过程中,创建了许多默认的RBAC规则, 在k8s有关RBAC的官方文档中,我们看到下面一些default clusterrole列表:
其中第一个cluster-admin这个cluster role binding绑定了system:masters group,这和authentication环节传递过来的身份信息不谋而合。 沿着system:masters group对应的cluster-admin clusterrolebinding“追查”下去,真相就会浮出水面。
我们查看一下这一binding:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 $ kubectl describe clusterrolebinding cluster-admin Name: cluster-admin Labels: kubernetes.io/bootstrapping=rbac-defaults Annotations: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: true Role: Kind: ClusterRole Name: cluster-admin Subjects: Kind Name Namespace ---- ---- --------- Group system:masters
我们看到在kube-system名字空间中,一个名为cluster-admin的clusterrolebinding将cluster-admin cluster role与system:masters Group绑定到了一起, 赋予了所有归属于system:masters Group中用户cluster-admin角色所拥有的权限。
我们再来查看一下cluster-admin这个role的具体权限信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 $ kubectl describe clusterrole cluster-admin Name: cluster-admin Labels: kubernetes.io/bootstrapping=rbac-defaults Annotations: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: true PolicyRule: Resources Non-Resource URLs Resource Names Verbs --------- ----------------- -------------- ----- *.* [] [] [*] [*] [] [*]
非资源类,如查看集群健康状态。
RBAC Role-Based Access Control,基于角色的访问控制, apiserver启动参数添加–authorization-mode=RBAC 来启用RBAC认证模式,kubeadm安装的集群默认已开启。官方介绍
查看开启:
1 2 3 4 $ ps -ef | grep apiserver root 6119 5911 7 8月25 ? 4-12:07:50 kube-apiserver --advertise-address=192.168.100.1 --allow-privileged=true --authorization-mode=Node,RBAC --client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt --enable-admission-plugins=NodeRestriction --enable-bootstrap-token-auth=true --etcd-cafile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt --etcd-certfile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.crt --etcd-keyfile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.key --etcd-servers=https://127.0.0.1:2379 --kubelet-client-certificate=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-kubelet-client.crt --kubelet-client-key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-kubelet-client.key --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname --proxy-client-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-client.crt --proxy-client-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-client.key --requestheader-allowed-names=front-proxy-client --requestheader-client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-ca.crt --requestheader-extra-headers-prefix=X-Remote-Extra- --requestheader-group-headers=X-Remote-Group --requestheader-username-headers=X-Remote-User --secure-port=6443 --service-account-issuer=https://kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local --service-account-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/sa.pub --service-account-signing-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/sa.key --service-cluster-ip-range=10.96.0.0/12 --tls-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.crt --tls-private-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.key aaron 1538613 1356648 0 17:55 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto apiserver
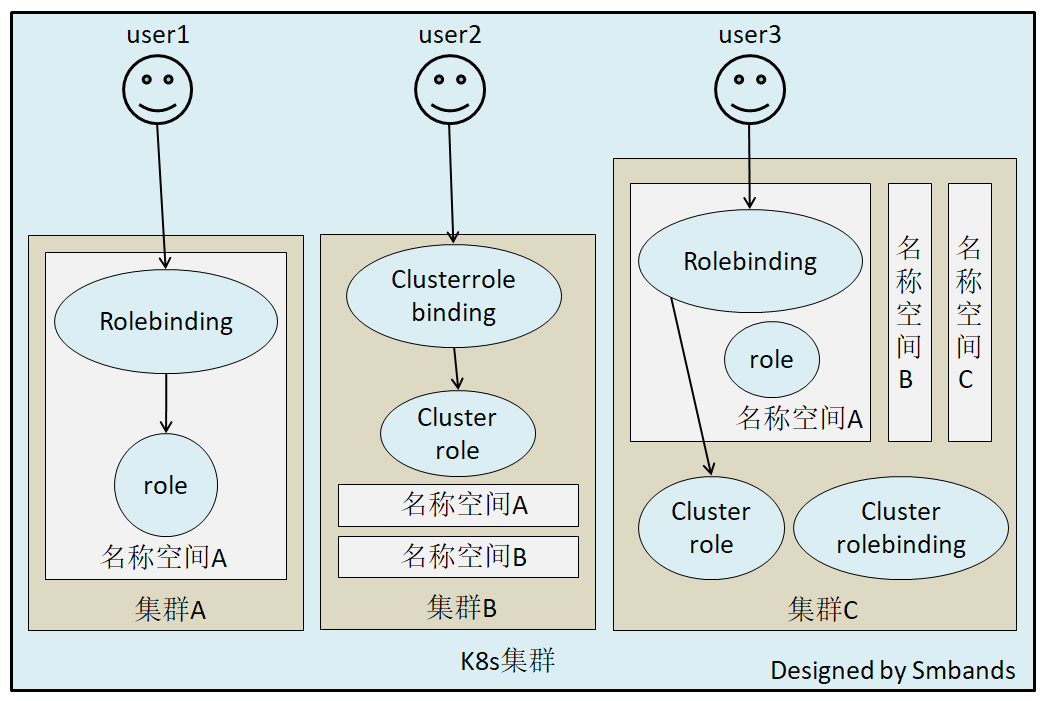
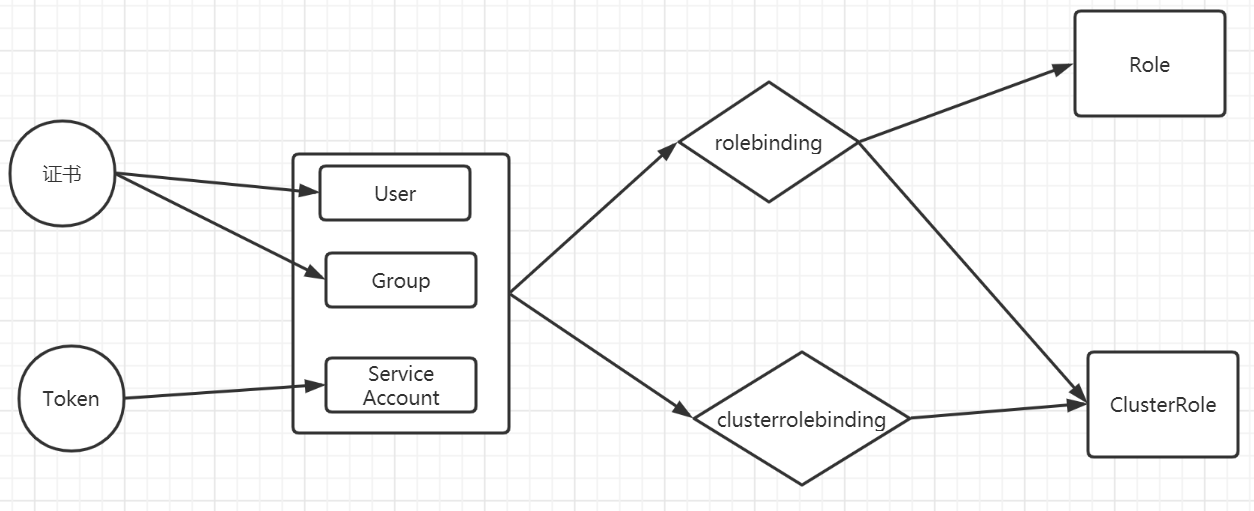
RBAC模式引入了4个资源类型:
Role,角色 一个Role只能授权访问单个namespace
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 kind: Role apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: namespace: demo name: pod-reader rules: - apiGroups: ["" ] resources: ["pods" ] verbs: ["get" , "watch" , "list" ]
ClusterRole 一个ClusterRole能够授予和Role一样的权限,但是它是集群范围内的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 kind: ClusterRole apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: secret-reader rules: - apiGroups: ["" ] resources: ["secrets" ] verbs: ["get" , "watch" , "list" ]
Rolebinding 将role中定义的权限分配给用户和用户组。RoleBinding包含主题(users,groups,或service accounts)和授予角色的引用。对于namespace内的授权使用RoleBinding,集群范围内使用ClusterRoleBinding。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 kind: RoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: read-pods namespace: demo subjects: - kind: User name: jane apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: secret-reader apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
注意:rolebinding既可以绑定role,也可以绑定clusterrole,当绑定rolebinding的时候,subject的权限也会被限定于rolebinding定义的namespace内部,若想跨namespace,需要使用clusterrolebinding
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: name: read-secrets namespace: development subjects: - kind: User name: dave apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io - kind: ServiceAccount name: dave namespace: test roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: secret-reader apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
考虑一个场景:如果集群中有多个namespace分配给不同的管理员,每个namespace的权限是一样的,就可以只定义一个clusterrole,然后通过rolebinding将不同的namespace绑定到管理员身上,否则就需要每个namespace定义一个Role,然后做一次rolebinding。
ClusterRolebingding 允许跨namespace进行授权
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: read-secrets-global subjects: - kind: Group name: manager apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: secret-reader apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kubelet的认证授权 查看kubelet进程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 $ systemctl status kubelet ● kubelet.service - kubelet: The Kubernetes Node Agent Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/kubelet.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d └─10-kubeadm.conf Active: active (running) since Fri 2023-08-25 15:17:30 CST; 1 month 28 days ago Docs: https://kubernetes.io/docs/ Main PID: 6229 (kubelet) Tasks: 18 (limit : 24810) Memory: 57.4M CPU: 2d 3h 57min 37.642s CGroup: /system.slice/kubelet.service └─6229 /usr/bin/kubelet --bootstrap-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/bootstrap-kubelet.conf --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf --config=/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml --container-runtime-endpoint=unix:///var/ru>
查看/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf,解析证书:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 $ sudo cat /etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf apiVersion: v1 clusters: - cluster: certificate-authority-data: ...... server: https://192.168.100.1:6443 name: kubernetes contexts: - context: cluster: kubernetes user: system:node:k8s-master name: system:node:k8s-master@kubernetes current-context: system:node:k8s-master@kubernetes kind: Config preferences: {} users :- name: system:node:k8s-master user: client-certificate: /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet-client-current.pem client-key: /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet-client-current.pem $ openssl x509 -in /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet-client-current.pem -text $ sudo openssl x509 -in /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet-client-current.pem -text Certificate: Data: Version: 3 (0x2) Serial Number: 625981109107871580 (0x8afee808c7acf5c) Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption Issuer: CN = kubernetes Validity Not Before: Aug 25 07:12:13 2023 GMT Not After : Aug 24 07:17:20 2024 GMT Subject: O = system:nodes, CN = system:node:k8s-master
得到我们期望的内容:
1 2 Subject: O=system:nodes, CN=system:node:k8s-master
我们知道,k8s会把O作为Group来进行请求,因此如果有权限绑定给这个组,肯定在clusterrolebinding的定义中可以找得到。因此尝试去找一下绑定了system:nodes组的clusterrolebinding
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 $ kubectl get clusterrolebinding -oyaml|grep -n10 system:nodes 91- name: kubeadm:node-autoapprove-certificate-rotation 92- resourceVersion: "252" 93- uid: 194ef397-1a05-47d8-8672-7d967f5e3d30 94- roleRef: 95- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io 96- kind: ClusterRole 97- name: system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:selfnodeclient 98- subjects: 99- - apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io 100- kind: Group 101: name: system:nodes 102-- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 103- kind: ClusterRoleBinding 104- metadata: 105- creationTimestamp: "2023-08-25T07:17:31Z" 106- name: kubeadm:node-proxier 107- resourceVersion: "282" 108- uid: ff410466-f2ad-47f7-9865-e3cdfbd34e8b 109- roleRef: 110- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io 111- kind: ClusterRole $ kubectl describe clusterrole system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:selfnodeclient Name: system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:selfnodeclient Labels: kubernetes.io/bootstrapping=rbac-defaults Annotations: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: true PolicyRule: Resources Non-Resource URLs Resource Names Verbs --------- ----------------- -------------- ----- certificatesigningrequests.certificates.k8s.io/selfnodeclient [] [] [create]
结局有点意外,除了system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:selfnodeclient外,没有找到system相关的rolebindings,显然和我们的理解不一样。 尝试去找资料 ,发现了这么一段 :
Default ClusterRole
Default ClusterRoleBinding
Description
system:kube-scheduler
system:kube-scheduler user
Allows access to the resources required by the scheduler component.
system:volume-scheduler
system:kube-scheduler user
Allows access to the volume resources required by the kube-scheduler component.
system:kube-controller-manager
system:kube-controller-manager user
Allows access to the resources required by the controller manager component. The permissions required by individual controllers are detailed in the controller roles .
system:node
None
Allows access to resources required by the kubelet, including read access to all secrets, and write access to all pod status objects . You should use the Node authorizer and NodeRestriction admission plugin instead of the system:node role, and allow granting API access to kubelets based on the Pods scheduled to run on them. The system:node role only exists for compatibility with Kubernetes clusters upgraded from versions prior to v1.8.
system:node-proxier
system:kube-proxy user
Allows access to the resources required by the kube-proxy component.
大致意思是说:之前会定义system:node这个角色,目的是为了kubelet可以访问到必要的资源,包括所有secret的读权限及更新pod状态的写权限。如果1.8版本后,是建议使用 Node authorizer and NodeRestriction admission plugin 来代替这个角色的。
我们目前使用1.19,查看一下授权策略:
1 2 3 4 $ ps axu|grep apiserver kube-apiserver --authorization-mode=Node,RBAC --enable-admission-plugins=NodeRestriction
查看一下官网对Node authorizer的介绍:
Node authorization is a special-purpose authorization mode that specifically authorizes API requests made by kubelets.
In future releases, the node authorizer may add or remove permissions to ensure kubelets have the minimal set of permissions required to operate correctly.
In order to be authorized by the Node authorizer, kubelets must use a credential that identifies them as being in the system:nodes group, with a username of system:node:<nodeName>
Service Account及 K8S Api 调用 前面说,认证可以通过证书,也可以通过使用ServiceAccount(服务账户)的方式来做认证。大多数时候,我们在基于k8s做二次开发时都是选择通过ServiceAccount + RBAC 的方式。我们之前访问dashboard的时候,是如何做的?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: admin namespace: kubernetes-dashboard --- kind: ClusterRoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: admin annotations: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true" roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-admin apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: admin namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
我们查看一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 $ kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get sa admin -o yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: creationTimestamp: "2020-04-01T11:59:21Z" name: admin namespace: kubernetes-dashboard resourceVersion: "1988878" selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/serviceaccounts/admin uid: 639ecc3e-74d9-11ea-a59b-000c29dfd73f secrets: - name: admin-token-lfsrf
注意到serviceaccount上默认绑定了一个名为admin-token-lfsrf的secret,我们查看一下secret
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 $ kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard describe secret admin-token-lfsrf Name: admin-token-lfsrf Namespace: kubernetes-dashboard Labels: <none> Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: admin kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: 639ecc3e-74d9-11ea-a59b-000c29dfd73f Type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token Data ==== ca.crt: 1025 bytes namespace: 4 bytes token: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9uYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJkZW1vIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9zZWNyZXQubmFtZSI6ImFkbWluLXRva2VuLWxmc3JmIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9zZXJ2aWNlLWFjY291bnQubmFtZSI6ImFkbWluIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9zZXJ2aWNlLWFjY291bnQudWlkIjoiNjM5ZWNjM2UtNzRkOS0xMWVhLWE1OWItMDAwYzI5ZGZkNzNmIiwic3ViIjoic3lzdGVtOnNlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50OmRlbW86YWRtaW4ifQ.ffGCU4L5LxTsMx3NcNixpjT6nLBi-pmstb4I-W61nLOzNaMmYSEIwAaugKMzNR-2VwM14WbuG04dOeO67niJeP6n8-ALkl-vineoYCsUjrzJ09qpM3TNUPatHFqyjcqJ87h4VKZEqk2qCCmLxB6AGbEHpVFkoge40vHs56cIymFGZLe53JZkhu3pwYuS4jpXytV30Ad-HwmQDUu_Xqcifni6tDYPCfKz2CZlcOfwqHeGIHJjDGVBKqhEeo8PhStoofBU6Y4OjObP7HGuTY-Foo4QindNnpp0QU6vSb7kiOiQ4twpayybH8PTf73dtdFt46UF6mGjskWgevgolvmO8A
只允许访问test命名空间的pod资源:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 $ cat test-admin-rbac.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: test-pods-admin namespace: test --- kind: Role apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: namespace: test name: pods-reader-writer rules: - apiGroups: ["" ] resources: ["pods" ] verbs: ["*" ] --- kind: RoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: pods-reader-writer namespace: test subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: test-pods-admin namespace: test roleRef: kind: Role name: pods-reader-writer apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
演示权限:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 $ kubectl -n test describe secrets test-pods-admin-token-prr25 ... token: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6InBtQUZfRl8ycC03TTBYaUUwTnJVZGpvQWU0cXZ5M2FFbjR2ZjkzZVcxOE0ifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9uYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJsdWZmeSIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VjcmV0Lm5hbWUiOiJsdWZmeS1hZG1pbi10b2tlbi1wcnIyNSIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VydmljZS1hY2NvdW50Lm5hbWUiOiJsdWZmeS1hZG1pbiIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VydmljZS1hY2NvdW50LnVpZCI6ImFhZDA0MTU3LTliNzMtNDJhZC1hMGU4LWVmOTZlZDU3Yzg1ZiIsInN1YiI6InN5c3RlbTpzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudDpsdWZmeTpsdWZmeS1hZG1pbiJ9.YWckylE5wlKITKrVltXY4VPKvZP9ar5quIT5zq9N-0_FnDkLIBX7xOyFvZA5Wef0wSFSZe3e9FwrO1UbPsmK7cZn74bhH8cNdoH_YVbIVT3-6tIOlCA_Bc8YypGE1gl-ZvLOIPV7WnRQsWpWtZtqfKBSkwLAHgWoxcx_d1bOcyTOdPmsW224xcBxjYwi6iRUtjTJST0LzOcAOCPDZq6-lqYUwnxLO_afxwg71BGX4etE48Iny8TxSEIs1VJRahoabC7hVOs17ujEm5loTDSpfuhae51qSDg8xeYwRHdM42aLUmc-wOvBWauHa5EHbH9rWPAnpaGIwF8QvnLszqp4QQ ... $ curl -k -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6InBtQUZfRl8ycC03TTBYaUUwTnJVZGpvQWU0cXZ5M2FFbjR2ZjkzZVcxOE0ifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9uYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJsdWZmeSIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VjcmV0Lm5hbWUiOiJsdWZmeS1hZG1pbi10b2tlbi1wcnIyNSIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VydmljZS1hY2NvdW50Lm5hbWUiOiJsdWZmeS1hZG1pbiIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VydmljZS1hY2NvdW50LnVpZCI6ImFhZDA0MTU3LTliNzMtNDJhZC1hMGU4LWVmOTZlZDU3Yzg1ZiIsInN1YiI6InN5c3RlbTpzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudDpsdWZmeTpsdWZmeS1hZG1pbiJ9.YWckylE5wlKITKrVltXY4VPKvZP9ar5quIT5zq9N-0_FnDkLIBX7xOyFvZA5Wef0wSFSZe3e9FwrO1UbPsmK7cZn74bhH8cNdoH_YVbIVT3-6tIOlCA_Bc8YypGE1gl-ZvLOIPV7WnRQsWpWtZtqfKBSkwLAHgWoxcx_d1bOcyTOdPmsW224xcBxjYwi6iRUtjTJST0LzOcAOCPDZq6-lqYUwnxLO_afxwg71BGX4etE48Iny8TxSEIs1VJRahoabC7hVOs17ujEm5loTDSpfuhae51qSDg8xeYwRHdM42aLUmc-wOvBWauHa5EHbH9rWPAnpaGIwF8QvnLszqp4QQ" https://10.209.0.13:6443/api/v1/namespaces/test/pods?limit =500
认证、鉴权图鉴
创建用户认证授权的 kubeconfig 文件 这里我们签发一个用户认证的kubeconfig文件。比如研发、测试想要使用kubectl访问k8s集群,但是又不想给他们root权限,就可以通过这种方式来做,因为一旦kubeconfig文件给出去了,再进行限制就难了。
签发证书对: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 $ openssl genrsa -out test.key 2048 $ openssl req -new -key test.key -out test.csr -subj "/O=admin:test/CN=test-admin" $ cat extfile.conf [ v3_ca ] keyUsage = critical, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment extendedKeyUsage = clientAuth $ openssl x509 -req -in test.csr -CA /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt -CAkey /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.key -CAcreateserial -sha256 -out test.crt -extensions v3_ca -extfile extfile.conf -days 3650
配置kubeconfig文件: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 $ kubectl config set-cluster test-cluster --certificate-authority=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt --embed-certs=true --server=https://10.209.0.13:6443 --kubeconfig=test.kubeconfig $ kubectl config set-credentials test-admin --client-certificate=test.crt --client-key=test.key --embed-certs=true --kubeconfig=test.kubeconfig $ kubectl config set-context test-context --cluster=test-cluster --user=test-admin --kubeconfig=test.kubeconfig $ kubectl config use-context test-context --kubeconfig=test.kubeconfig
权限绑定 1 2 3 4 5 6 $ export KUBECONFIG=test.kubeconfig $ kubectl get po Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "test-admin" cannot list resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "default"
为test-admin用户添加test命名空间访问权限:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 $ cat test-admin-role.yaml apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: namespace: test name: test-admin rules: - apiGroups: ["*" ] resources: ["*" ] verbs: ["*" ] $ cat test-admin-rolebinding.yaml apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: name: test-admin namespace: test subjects: - kind: User name: test-admin apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io roleRef: kind: Role name: test-admin apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io $ kubectl create -f test-admin-role.yaml $ kubectl create -f test-admin-rolebinding.yaml
测试 此时,使用用户test-admin,就可以访问test命名空间的资源了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 $ kubectl get po Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "test-admin" cannot list resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "default" $ kubectl get po -n test NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE myblog-84985b5b66-jp9gg 1/1 Running 0 54d myblog-84985b5b66-smpwb 1/1 Running 0 54d mysql-7f97cb6cc9-vzxpd 1/1 Running 0 55d testpod-865855cfc5-m2f99 1/1 Running 0 42d
小技巧总结 快速反查 ServiceAccount 比如我们查看system:masters这个集群角色绑定的用户,可以通过以下命令快速找到对应字段并且获取一些相关信息:
1 $ kubectl describe clusterrolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io -o yaml|grep -n15 system:masters